Plastic injection moulding is a popular, highly effective manufacturing process to create accurate, high quality plastic component that are used across a wide range of industries. From automotive to medical ; construction to heavy industry, plastic moulding supplies are used across almost every application. The process requires different plastic moulding supplies to work. From machine parts using different metals to the polymers that are poured into the hopper, melted and moulded, here is the lowdown on some of them.
What Plastic Moulding Supplies Are Required?
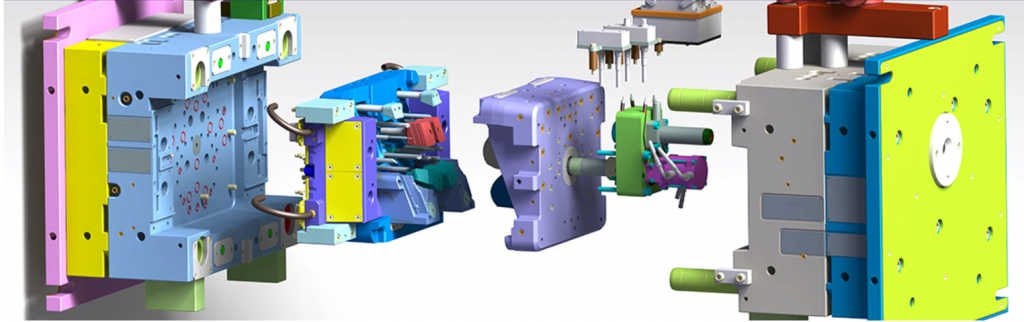
The injection moulding machine itself is comprised of three parts: the injection unit, the mould itself and the clamp. Each part is carefully designed to produce plastic units that meet precise specifications and quality control measures. Products must follow strict requirements around the type of plastic used, the shape and size of the finished product and the properties that the finished piece must display.
For instance, a part to be installed into industrial equipment must have excellent corrosion resistance, not be prone to warping and be able to withstand heavy use. Plastic parts created for packaging or branding must look aesthetically pleasing with the correct colour, finish and printing applied. Here are some of the plastic moulding supplies and parts needed to create robust, attractive parts that are fit for purpose and meet customer expectations.
Plastic Moulding Machine Processes
A plastic injection moulding machine operates through several processes, with each one requiring specialist plastic moulding supplies to work:
· Clamping
· Injection into mould
· Cooling of product
· Mould opening
· Product removal
The clamping and injection stages are processed by separate units – the clamping unit and injection unit. Plastic pellets are poured into a hopper and clamped in place before being melted by the injection unit. This is then plunged into a mould, which has been specially shaped to match the project requirements. Moulds are metal blocks made from steel, stainless steel, copper alloy or aluminium.
The metal is chosen to suit whatever the machine is required to produce. For example, aluminium is ideal for low volume, larger parts, while steel is better for high volumes as it is less susceptible to damage. Whichever metal supplies are chosen, they must be able to withstand the high temperatures of the molten plastic without warping or breaking mid-cycle.
The plastic is then allowed to settle inside the mould while removing any air bubbles and correcting any mistakes. It is cooled until it hardens into the right shape. The injection moulding machine will have been carefully adjusted to produce the correct appearance, dimensions and mechanical properties needed in the completed plastic component. The clamping force and injection pressure will also have been meticulously calibrated to create the desired effect.
After that, the mould opens and the product is ejected, again using various plastic moulding machine supplies to enable the process. The product is checked for quality and then moved on to the next stage in the supply chain. Meanwhile, any excess plastic is collected to be used in a future product.
Plastic Moulding Polymer Supplies
The most commonly used plastic injection moulding processes involve thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers. These can produce a wide variety of products, from rigid plastic toys and tools to flexible food and beverage packaging. Thermoplastics are recyclable, very versatile and easy to soften and shape while heated. Some elastomers are also used in plastic injection moulding, although this is less common.
Some common thermoplastics include PET (polyethylene terephthalate), which is commonly used for packaging and applications requiring robust hygienic properties and an attractive finish. PP (polypropylene) is used in textiles and packaging as it is chemical resistant and versatile. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a soft, flexible plastic also used in textiles and packaging, as well as signage and plastic bottles.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a tough, transparent plastic with an attractive glasslike finish. It is favoured for cosmetics packaging, e.g. lipstick and mascara cases. It can also be produced in a clear finish or coloured to match branding. Also prized in the beauty world is Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN), a rigid, transparent and durable polymer used to make pots and jars for cosmetic creams, waxes, serums and lotions. Each plastic is carefully chosen to suit the required purpose.